
Scientists baffled after discovering that the Earth's core is 'leaking'
The name “core” suggests something hard and fixed but, it turns out, the Earth’s core is leaking. That is, at least, according to a team of top scientists, who drew the conclusion after analysing 62-million-old Arctic rocks. Geochemists from the California Institute of Technology and Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution detected record concentrations of helium 3 (3He) and helium 4 (4He) isotopes in the rocks, which suggest a slow trickle up from the very heart of our planet. They believe there could be reserves of the elusive gas buried some 2,900km underground. Helium is a surprisingly rare element on the Earth’s surface and experts have yet to establish just how much of it remains trapped deep beneath our feet. However, the new discovery has provided them with a fresh insight into the most mysterious region of our world. Understanding the presence of these helium isotopes could illuminate key processes in the core, such as how the Earth generated its life-protecting magnetic field. Most helium in the universe dates back to the Big Bang which occurred 13.8 billion years ago. The Earth swallowed up some of this as an infant planet, but mostly burped it all away during its 4.6 billion-year-long formation, as Science Alert reports. This means that any traces of helium found in volcanic rock – such as the samples unearthed in the Arctic – are believed to come either from pockets of mantle that are yet to release their helium, or from a vast, slow-leaking reserve. Basaltic lavas on Canada's Baffin Island contain some of the world's highest ratios of 3He to 4He, which geologists believe indicates that the gas's presence is not to do with the atmosphere, but rather the sign of deeper terrestrial origins. Several years ago, geochemist Forrest Horton uncovered helium isotope ratios of up to 50 times that of atmospheric levels in samples collected from Baffin's lava fields. This unusual concentration was also detected in lavas collected from Iceland. Horton and his team wondered if the helium in both samples may have derived from an ancient reservoir deep within the crust. And, it seems, their hunch may have been right. Their latest analysis – including specimens of the mineral olivine taken from dozens of sites across Baffin and surrounding islands – has delivered the highest ratio of 3He to 4He ever recorded in volcanic rock – measuring nearly 70 times anything previously detected in the atmosphere, as Science Alert notes. The team also considered ratios of other isotopes in order to rule out factors that may have altered the helium’s composition post-volcanic eruption, and found that the ratio of isotopes in the gas neon also matched the conditions present during the Earth’s formation. Despite advances in geology, the Earth’s core remains a great mystery, given that we have no way of directly exploring its core. The deepest hole humans have ever dug – branded the "entrance to hell" – extended an impressive 12,263m (40,230ft) down, but even that doesn’t come close to breaking through the crust to the layers beneath. Still, thanks to techniques like seismic tomography – which analyses how waves of energy travel through different materials during earthquakes – we’ve been able to map out the world’s interior. And carefully crafted simulations, based on the thermodynamics and pressures of our planet’s innards, suggest reserves of noble gases (like helium and neon) trapped in the core could have been protected as the Earth grew before seeping into the surrounding mantle over time. If the core is leaking, this could teach us a thing or two about how planets like ours form and how life, eventually, emerges. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings
2023-10-23 17:21

SpaceX signs deal to launch key European satellites - WSJ
SpaceX has signed a deal to launch up to four of Europe's flagship navigation and secure communications satellites
2023-10-23 16:53

Japan auto show returns, as industry faces EV turning point
By Daniel Leussink TOKYO Tokyo's auto show is back for the first time in four years and newly
2023-10-23 16:18

Foxconn faces China tax probe amid Taiwan election - sources
By Yimou Lee and Ben Blanchard TAIPEI (Reuters) -Foxconn, a major supplier of Apple's iPhones, is facing a tax probe
2023-10-23 13:22

Astronomers have just discovered an 8 billion-year-old radio signal
An eight billion-year-old radio signal containing extreme levels of energy has been discovered by astronomers. According to the journal Science, a “fast radio burst” was recorded as lasting for just a millisecond. The radio-frequency electromagnetic radiation was identified as FRB 20220610A, and it contained a truly staggering level of energy – releasing the same amount that the sun releases in 30 years. As CNN reports, the true nature of these blasts can often be hard to determine, given that they last for such a short length of time. It is believed, however, that they result from galaxies merging to create new stars. Furthermore, they could also be 'weighed', in order to measure the mass of the elements in the universe which are found between galaxies and unaccounted for. Coauthor Ryan Shannon said: “If we count up the amount of normal matter in the universe - the atoms that we are all made of - we find that more than half of what should be there today is missing. “We think that the missing matter is hiding in the space between galaxies, but it may just be so hot and diffuse that it’s impossible to see using normal techniques.” The huge signal was discovered using the Australian SKA Pathfinder radio telescope, before further observation was undertaken using a telescope in China – which was able to determine that the fast radio burst was the oldest and more remote example discovered to date. It comes after scientists were left baffled following the discovery of a mysterious object which sends radio waves every 21 minutes earlier this year. The really strange thing is, it’s been doing the same thing for 45 years and astronomers are still unsure about what it could be. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings
2023-10-22 23:21
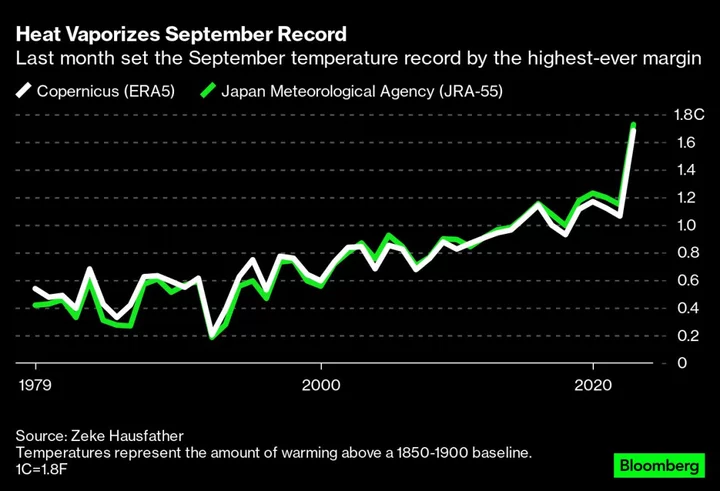
Asset Managers Are Updating Bond Models to Capture a New Risk
A growing number of asset managers is reassessing bond values tied to real assets, as a spike in
2023-10-22 21:22
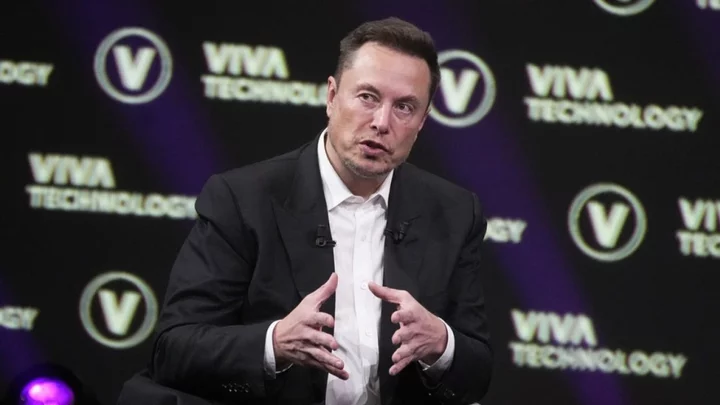

Former Twitter employee says working for Elon Musk was ‘hardest experience of her life’
A former employee of Twitter/X has spoken about the working conditions under Elon Musk, claiming that it was the ‘hardest experience of her life’. The social media platform’s head of trust and safety, Ella Irwin, resigned from the company in June, confirming the decision to Reuters. Her decision to leave the company came after Musk doubled down on his stance on trans issues, confirming he would be lobbying legislators to “criminalise making severe, irreversible changes to children below the age of consent” through gender-affirming surgery, and that “nobody knows who they are as a child”. Writing in June, Irwin said that it had become clear “there was no longer alignment” between her “nonnegotiable principles” and the policies of Twitter/X. Now, Irwin has spoken further about her decision and criticised the “terrible” decisions made by Musk. Irwin released a statement to NBC News, saying: “It absolutely was the hardest experience that I've gone through in my career. Speaking about Musk’s decision making, Irwin said: “There's more emotion behind his decisions than I would have maybe expected before I met him. “I think that contributes to some of the impulsiveness… I think there were a lot of situations in which I would have handled things very differently.” Reflecting on Musk’s leadership, Irwin added: “There were things that I wouldn't have tweeted in the middle of the night, [and] there were certainly things that could have been stated better.” It comes after Kanye West accused Musk of taking advantage of his clout in a bid to boost the “struggling” platform’s numbers. West is used to causing outrage on Twitter/X, having been banned from the platform in the past. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings
2023-10-22 16:49
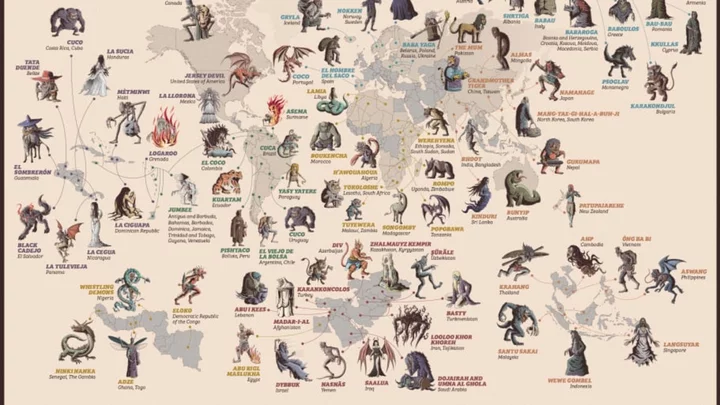
Map Shows Local Versions of The Boogeyman From Around the World
From Kelpie to Krampus, get to know these boogeymen (and boogeywomen) from different countries.
2023-10-22 05:22
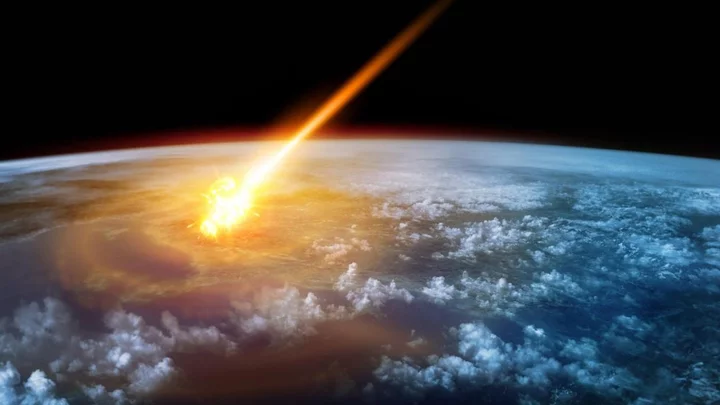

Meteor crashes through man's roof and he sells it for millions
A man had a meteor crash through his roof. Now he's a millionaire. Josua Hutagalung was stunned when a space rock crashed into his home in Kolang, Indonesia. Hutagalung was working outside when the meteor smashed through his veranda next to the living room. It managed to bury itself 15cm deep in the soil. The meteor turned out to be 4.5 billion years old, weighing 2.1kg, boasting a price tag of £1.4 million. It was classified as an extremely rare CM1/2 carbonaceous Chondrite. The meteor was bought by a specialist collected for the equivalent to 30 years' salary. Talking of his newfound wealth, Hutagalung said he wanted to use it to build a church in his community. "I have also always wanted a daughter," he told The Sun, saying he saw the meteor as a "sign that I will be lucky enough now to have one". Three other fragments of the meteor were also found nearby. After it was bought from a collector in Indianapolis, the meteorite was shipped to the US. Jared Collins, a meteorite expert from America, who bought part of the rock, said: "My phone lit up with crazy offers for me to jump on a plane and buy the meteorite. "It was the middle of the Covid crisis and frankly it was a toss-up between buying the rock for myself or working with scientists and collectors in the US. "I carried as much money as I could muster and went to find Josua, who turned out to be a canny negotiator." Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-10-22 00:23

Web Summit CEO resigns after recent comments on Israeli conflict
Web Summit Chief Executive and founder Paddy Cosgrave on Saturday resigned after comments he made on the Israeli-Hamas
2023-10-21 23:17
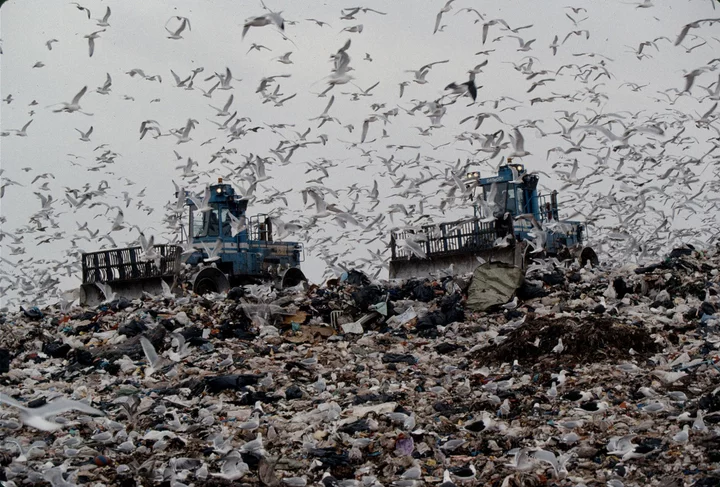

How New York City Turned the World’s Biggest Garbage Dump Into a Park
Staten Island’s Freshkills was once the world’s largest dump. In 2001, New York City shut it down and
2023-10-21 21:50
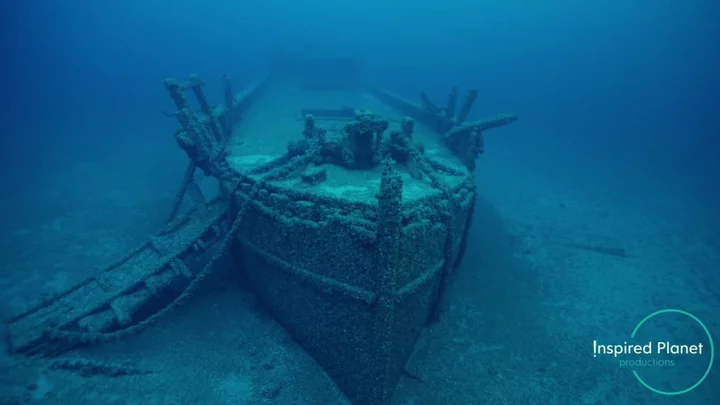

Huge shipwreck discovered after 128 years by crew making a nature documentary
A massive shipwreck which hasn’t been seen since it sank 128 years ago has been discovered by a crew making a nature documentary. Filmmakers were working on a project about a mussel species which lives in the Great Lakes in the US when they made the unexpected find. Yvonne Drebert and Zach Melnick were researching the invasive quagga mussel when they stumbled upon the steamship Africa, Fox Weather reports. The ship was sunk in 1895 after travelling from Ohio to Ontario on Lake Huron in dangerous conditions. The wreck was found after the filmmakers’ underwater drone detected something big and a camera was sent down to take a look. “It got more and more definition as we got closer and closer, and all of a sudden, we could see, ‘Wow, this is a steamship, a wooden steamship!'” Melnik said. “So this is old, and it is incredibly well intact.” The discovery was made possible due to the mussel species, which had covered the wreckage. The ship was identified as the Africa. Since the discovery, families of the people who were lost on board have been in touch with the filmmakers. “One of the incredible things that’s happened since this story has come to light just a couple of weeks ago is that several of the descendants of family members who died on this wreck so many years ago have reached out to us,” Melnick said. “We’re working with those families to try to find a way to remember those sailors who had died 128 years ago.” The mussel species will eventually destroy the wreckage, and the quagga can be hugely damaging to natural environments. The Center of Invasive Species Research in Riverside, California, reports that quagga [and zebra mussels] invasions “have had catastrophic impacts in the ecosystems in which they have established.” “These organisms clog water intake structures (e.g., pipes and screens), which greatly increases maintenance costs for water treatment and power plants,” the organization adds on its website. “Recreational activities on lakes and rivers are adversely affected as mussels accumulate on docks, buoys, boat hulls, anchors and beaches can become heavily encrusted.” “Interestingly, invasions by quagga and zebra mussels have been documented as having some positive affects on receiving ecosystems. For example, filtration of water by mussels as they extract food removes particulate matter. This filtration has improved water clarity, and reduced the eutrophication of polluted lakes.” Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings
2023-10-21 17:51
