Alphabet’s $118 Billion Cash Pile Poses a New Problem
Alphabet Inc. is facing a new and, by most accounts, welcome problem — how to spend its rapidly
2023-08-11 17:53

Energy Department announces largest-ever investment in 'carbon removal'
The Department of Energy announced Friday it is awarding up to $1.2 billion to two projects that promise to remove carbon dioxide from the air in what officials said was the largest investment in “engineered carbon removal” in history
2023-08-11 17:16

Adin Ross’ 'gay son or thot daughter' question to YouTuber Charleston White leaves Internet ROFLING
Adin Ross’ 'gay son or thot daughter' question to YouTuber Charleston White leaves internet laughing
2023-08-11 16:58

ChatGPT fever spreads to US workplace, sounding alarm for some
By Richa Naidu, Martin Coulter and Jason Lange LONDON/WASHINGTON Many workers across the U.S. are turning to ChatGPT
2023-08-11 16:55

Italy signs preliminary deal with KKR to take up to 20% of TIM's grid
MILAN (Reuters) -The Italian government could end up with a stake of as much as 20% in Telecom Italia's landline
2023-08-11 16:47

Chinese tech giant Huawei reports sales, profit up despite US sanctions
Chinese tech giant Huawei says its revenue rose 3% over a year earlier and its profit margin widened in the first half of 2023 despite sanctions that limit its access to U.S. processor chips
2023-08-11 16:29

Odd ‘demon’ particle found inside superconductor may help demystify ‘holy grail’ of physics
Scientists have finally found a “demon” subatomic particle that was predicted to exist nearly seven decades ago and speculated to play an important role in the behaviours of a range of metals and alloys, including superconductors. Physcist David Pines in 1956 theorised that electrons, which normally have a mass and negative electric charge, can under some conditions combine to form a composite “demon” particle that is massless, neutral and does not interact with light. These theorised interesting properties, however, made these particles elude detection – until now. After a nearly 70-year search for these subatomic entities, researchers, including those from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, have finally found signatures of Dr Pines’ “demon” particles in the metal strontium ruthenate. “Demons have been theoretically conjectured for a long time, but experimentalists never studied them. In fact, we weren’t even looking for it. But it turned out we were doing exactly the right thing, and we found it,” study co-author Peter Abbamonte said. Electrons – which are distributed in different energy bands within atoms – are known to lose their individuality in solids with electric interactions making the particles combine to form collective units. With some threshold energy, studies have also shown electrons can form composite particles called plasmons with a new charge and mass. However, the mass is so large that these plasmon particles cannot form with the kind of energies available at room temperature. Revelations on room-temperature semiconductors are considered to be one of the “holy grails” of physics. But Dr Pines theorised that if a solid has electrons in more than one energy band, as many metals do, their respective plasmons may combine in an out-of-phase pattern to form a new plasmon that is massless and neutral – a demon. Since these special particles are massless, he argued they can form with any energy and may exist at all temperatures – leading to speculation that the demons have important effects on the behaviour of some metals with multiple energy bands. “The vast majority of experiments are done with light and measure optical properties, but being electrically neutral means that demons don’t interact with light,” Dr Abbamonte explained. So a completely new experiment was needed to detect them. In the research, scientists were studying the compound strontium ruthenate as it is similar to high-temperature superconductors – a special kind of material where electrical resistance vanishes. For a survey of the metal’s electronic properties, they synthesised high-quality samples of the metal. They then applied a technique to study the metal that uses energy from electrons shot into the metal to directly observe the metal’s features, including plasmons that form. During their observation of the electron interactions, scientists found something unusual – an electronic mode with no mass. “At first, we had no idea what it was. Demons are not in the mainstream. The possibility came up early on, and we basically laughed it off. But, as we started ruling things out, we started to suspect that we had really found the demon,” Ali Husain, another author of the study, said. Researchers then sought to calculate how electrons are distributed across bands inside strontium ruthenate. Predictions by Dr Pines indicate there are specific conditions when “demons” are likely to form, and it remained unknown whether strontium ruthenate would have the particle. “We had to perform a microscopic calculation to clarify what was going on. When we did this, we found a particle consisting of two electron bands oscillating out-of-phase with nearly equal magnitude, just like Pines described,” found Edwin Huang, another author of the study. “Our study confirms a 67-year-old prediction and indicates that demons may be a pervasive feature of multiband metals,” scientists wrote in the study. Read More Superconductor breakthrough could represent ‘biggest physics discovery of a lifetime’ – but scientists urge caution LK-99: Excitement rises over possibly revolutionary ‘miracle material’ – but there is still no good reason to believe it exists Superconductivity: The technology that could change everything if we just knew how it worked ‘Vampire child’ with padlocked ankle unearthed in Polish ‘necropolis’ Two new kinds of mole discovered in mountains of Turkey Scientific discovery casts doubt on our understanding of human evolution
2023-08-11 16:27
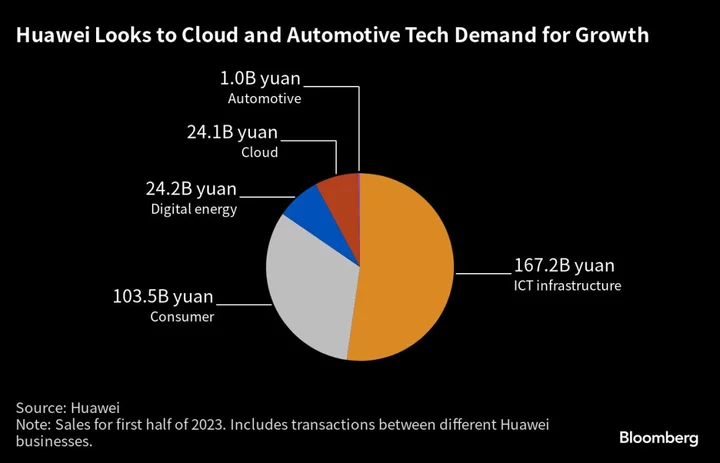
Huawei’s Sales Grow Again as New Arenas Mitigate Sanctions Hit
Huawei Technologies Co. grew sales for a third straight quarter, after new businesses like cloud services and a
2023-08-11 16:25

Astronomer uncovers ‘direct evidence’ of gravity breaking down in the universe
A scientist claims to have discovered a “gravitational anomaly” that calls into question our fundamental understanding of the universe. Astronomer Kyu-Hyun Chae from the university of Sejong University in South Korea made the discovery while studying binary star systems, which refer to two stars that orbit each other. His observations appear to go against the standard gravitational models established by Isaac Newton and Albert Einstein, and instead offer evidence that an alternative theory first proposed in the 1980s may explain the anomaly. Analysis of data collected by the European Space Agency’s Gaia space telescope revealed accelerations of stars in binaries that did not fit the standard gravitational models. At accelerations of lower than 0.1 nanometres per second squared, the orbit of the two stars deviated from Newton’s universal law of gravitation and Einstein’s general relativity. Instead, Professor Chae theorised that a model known as Modified Newtonian Dynamics (MOND) could explain why these previous theoretical frameworks were unable to explain the stars’ movements. “The deviation represents a direct evidence for the breakdown of standard gravity at weak acceleration,” Professor Chae wrote in a paper, titled ‘Breakdown of the Newton-Einstein standard gravity at low acceleration in internal dynamics of wide binary stars’, that was published in The Astrophysics Journal.. His research calls into question the existence of dark matter and other peculiar space phenomena that are typically used to justify irregularities with Newton-Einstein standards. “The data reveal an unambiguous and extremely strong signature of the breakdown of the standard Newton-Einstein gravity at weak acceleration,” the study concluded. “What is even more surprising is that the trend and magnitude of the gravitational anomaly agree with what the AQUAL [MOND] theory predicts.” Professor Chae predicts that his results will be confirmed and refined with larger data sets in the future, which could lead to a new revolution in physics. “Chae’s finding is a result of a very involved analysis of cutting-edge data, which, as far as I can judge, he has performed very meticulously and carefully,” said theoretical physicist Mordehai Milgrom at the Weizmann Institute in Israel, who first proposed the MOND model 40 years ago. “But for such a far-reaching finding – and it is indeed very far-reaching – we require confirmation by independent analyses, preferably with better future data. “If this anomaly is confirmed as a breakdown of Newtonian dynamics, and especially if it indeed agrees with the most straightforward predictions of MOND, it will have enormous implications for astrophysics, cosmology, and for fundamental physics at large.” Pavel Kroupa, professor at Charles University in Prague, added: “The implications for all of astrophysics are immense.” Read More Perseids 2023: Meteor beacon offers unique way to observe spectacular shower over UK Slack announces its biggest ever update Why you might never have to remember your password again AI can predict Parkinson’s subtype with up to 95% accuracy, study suggests
2023-08-11 15:52

'Super happy' Andrew Tate stuns fans by 'bragging' net worth in new tweet, trolls say 'let's be realistic here'
Andrew Tate gets joyous over finding 3 grand in the pocket of his old jeans
2023-08-11 15:22

Kai Cenat goes online for first time after Union Square giveaway riot, receives support from fans as he condemns rioters: 'That s**t is not cool'
Kai Cenat said, 'I had good intentions for this whole thing and none only that but I don't condone any of the things that went on that day'
2023-08-11 15:20

Maui Death Toll Climbs to 53 with Wildfire 80% Contained
The death toll in the fast-moving fire that leveled historic Lahaina on the West Maui coast rose to
2023-08-11 14:28
