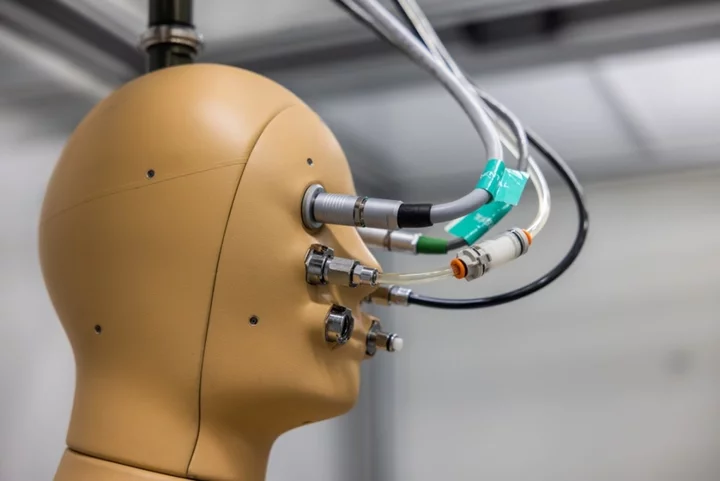

Scientists invent first ever ‘breathing, sweating, shivering’ robot
Scientists say they have built the first ever “breathing, sweating, shivering” robot, designed to cope and adapt to different temperatures. The heat-sensitive “thermal mannequin”, dubbed ANDI, features 35 individually controlled surfaces with pores that bead sweat like humans. Designed by US firm Thermetrics for use by researchers at Arizona State University, the robot was created to help better understand the health impacts of extreme temperatures on the human body. “ANDI sweats, he generates heat, shivers, walks and breathes,” said Konrad Rykaczewski, principal investigator for the ASU research project, whose work aims to identify and measure the effects of extreme heat on humans. “There’s a lot of great work out there for extreme heat, but there’s also a lot missing. We’re trying to develop a very good understanding of how heat impacts the human body so we can quantitatively design things to address it.” Some of the 10 sweating robots built by the researchers are already being used by clothing companies for garment testing, however ASU’s android is the only one that can be used outdoors. This allows experiments in previously impossible extreme heat environments, as well as studies into the impact of solar radiation. ASU researchers plan to test ANDI in heat-vulnerable areas around Phoenix this summer in an effort to understand how different ages and body types are impacted by high temperatures. “We can move different BMI models, different age characteristics and different medical conditions [into ANDI],” said Ankit Joshi, an ASU research scientist leading the modelling work and the lead operator of ANDI. “A diabetes patient has different thermal regulation from a healthy person. So we can account for all this modification with our customised models.” The results will be used to design interventions, such as cooling clothes and technologies to protect against heat stroke and heat-related deaths. Read More Electric cars could save more than 100,000 lives, study claims Electric cars could save more than 100,000 lives, study claims ‘I saw the future. It left me in tears’ This could be the end of ‘ducking’
2023-06-08 01:46

What Time Does Valorant June Night Market Start?
Valorant June Night Market starts on June 7 at 8 p.m. ET. Fans will have until June 27 to purchase their randomized gun skins.
2023-06-08 01:45
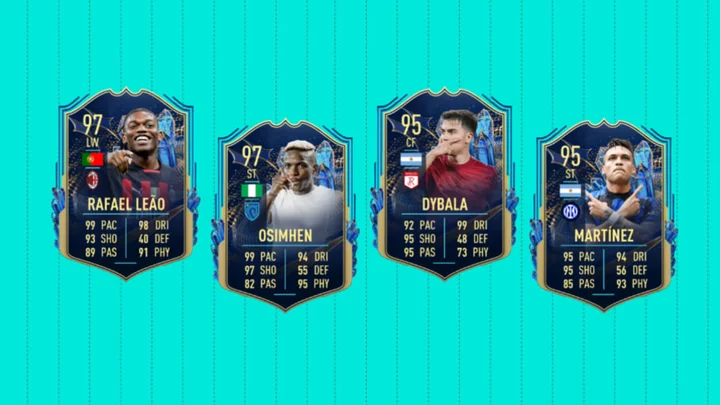
FIFA 23 Serie A TOTS Upgrade SBC: How to Complete
FIFA 23 Serie A TOTS Upgrade SBC is now live requiring two segments. Here's how to complete the SBC and if it's worth it.
2023-06-08 01:25

Russian-speaking cyber gang claims credit for hack of BBC and British Airways employee data
A group of Russian-speaking cyber criminals has claimed credit for a sweeping hack that has compromised employee data at the BBC and British Airways and left US and UK cybersecurity officials scrambling to respond.
2023-06-08 01:22

Altman Says AI Can Improve Government Service and Deserves Backing
Countries such as India should back research on artificial intelligence in ways that can improve government services like
2023-06-08 00:50

BT CEO pay to be frozen until retirement - Sky News
(Reuters) -BT Group's CEO Philip Jansen is to freeze his salary of 1.1 million pounds ($1.4 million) until he retires
2023-06-08 00:26

Kirk Cousins caught a vicious stray in the Madden 24 trailer
The winner of Madden 24 is all too obvious: Josh Allen. The loser is a fellow NFL quarterback who body-slammed by the Madden 24 trailer: Kirk Cousins.Minnesota Vikings quarterback Kirk Cousins could hardly be considered the villain of the NFL. So why did Madden 24 have to do him so dirty?The...
2023-06-08 00:19

FIFA Can’t Call 2022 World Cup Carbon-Neutral, Regulator Rules
Almost six months after Qatar hosted what it billed as a “carbon-neutral” World Cup, Switzerland’s advertising regulator ruled
2023-06-07 23:55

World Series of Warzone Twitch Drops: How to Claim
Fans can earn and claim free Twitch drops, like Double XP Tokens, Emblems, and Calling Cards, as they watch the World Series of Warzone.
2023-06-07 23:54

Better Safe Than Sorry: How to Run a Security Checkup on Your Google Account
Like a lot of people, your online life is probably heavily tied to Google, from
2023-06-07 23:47

When is the World Series of Warzone Final?
50 Trios will battle for their spot in the World Series of Warzone Grand Finals today in the Stage 1 NA Final at 1 p.m. ET.
2023-06-07 23:45

Astronomers have discovered a ‘treasure trove’ hidden 17 million light-years away
Astronomers have discovered a ‘treasure trove’ after capturing an image of a barred spiral galaxy located 17 million light-years away. The findings were made after the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) gave a more in depth look at galaxy NGC 5068. The feature is found in the constellation of Virgo, and it’s thought that the discovery could lead scientists to discover more about barred spiral galaxies like our own. The observations are all part of a series of findings from the JWST, with the telescope having collected images of 19 galaxies to add to our understanding of star-birthing galaxies. The bars can be seen in the upper left-hand section of the image posted by NASA below and they’re made up of tightly clustered stars. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter It’s thought that structures like these take as long as two billion years to form, which could mean they’re a lot older than other galaxies. “This image of the central, bright star-forming regions of the galaxy is part of a campaign to create an astronomical treasure trove, a repository of observations of star formation in nearby galaxies,” Webb astronomers said, via sci.news. “These observations are particularly valuable to us for two reasons. The first is because star formation underpins so many fields in astronomy, from the physics of the tenuous plasma that lies between stars to the evolution of entire galaxies.” “By observing the formation of stars in nearby galaxies, we hope to kick-start major scientific advances with some of the first available data from Webb.” It continued: “The second reason is that Webb’s observations build on other studies using telescopes including the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope and ground-based observatories.” They went on to say: “With its ability to peer through the gas and dust enshrouding newborn stars, Webb is particularly well-suited to explore the processes governing star formation. “Stars and planetary systems are born amongst swirling clouds of gas and dust that are opaque to visible-light observatories like Hubble or VLT.” Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-06-07 23:28
