
Masimo Announces Full Market Release of Stork™ Smart Home Baby Monitor
IRVINE, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 23, 2023--
2023-08-23 20:23

Options Appoints Former TNS and ICE Executive, Scott Feagans, as SVP of Sales Engineering
LONDON & NEW YORK & HONG KONG--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 23, 2023--
2023-08-23 19:57

IntelliGuard Appoints Robert Howard as CEO and Thomas Koning as President to Execute on Strategy of Continued Growth
SAN DIEGO, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 23, 2023--
2023-08-23 19:27

Scientists discover that plants make sounds when hurt that you can hear
Plants make sounds when they’re distressed and humans are only hearing them now for the first time, scientists have found. New research has discovered that sounds are used by plants to communicate with their ecosystems – and they could be studied and used to improve growing conditions for plants in the future. Itzhak Khait of Tel Aviv University led the research, which involved studying tobacco and tomato plants. As the findings showed, the plants made high-frequency noise which could be detected five metres away. The study was published in the journal Cell, and the results “can alter the way we think about the plant kingdom, which has been considered to be almost silent until now”. Not only that, but by studying the sounds emitted by the plants experts could tell whether they were in need of water or suffering from cuts. Lilach Hadany, an evolutionary biologist at Tel Aviv University, told Vice: “We started this project from the evolutionary question: why are plants mute? It appears that plants could have a lot to benefit from acoustic communication.” “We were particularly happy that the sounds turned out to be informative – containing information on the type of the plant and the type of the stress.” The findings could change the way plants are grown and communicate with their environments in future, given that we now know information can be conveyed via the sounds. Hadany went on to say: “What we do know is that there are sounds in the air, and they contain information. “Thus, natural selection may be acting on other organisms (animals and plants) to whom the sounds are relevant, to be able to hear the sounds and interpret them. That includes animals that can hear the sounds and can use the information to choose a food source or a laying site, or potentially plants that can prepare for the stress.” The team said in the study: “Plant sound emissions could offer a way for monitoring crops water and possibly disease states—questions of crucial importance in agriculture. “In times when more and more areas are exposed to drought due to climate change, efficient water use becomes even more critical, for both food security and ecology.” Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-23 19:27

SpyCloud Raises $110 Million Growth Round Led by Riverwood Capital to Accelerate Identity Threat Protection
AUSTIN, Texas--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 23, 2023--
2023-08-23 18:46

Children's advocates ask FTC to investigate Google for targeting ads to kids
Children's advocacy groups including Fairplay and Common Sense Media are asking the Federal Trade Commission to investigate Google, saying the tech giant serves personalized ads to kids on YouTube despite federal law prohibiting the practice
2023-08-23 18:18

AI eye scans can detect Parkinson’s up to seven years before symptoms appear, scientists say
Scientists have developed eye scans that use artificial intelligence to detect markers of Parkinson’s disease seven years before symptoms appear, making it the first time the condition can be detected several years before diagnosis. Parkinson disease’s is a deteriorating neurological condition characterised by a reduction of dopamine. The research, published on Tuesday in the journal Neurology, used two large sets of health data – the AlzEye dataset and the UK Biobank database – to identify these subtle markers, even though Parkinson’s disease has a relatively low prevalence among this population. The AlzEye dataset was formed from the world’s largest database of retinal images and associated clinical data. Post-mortem examination of Parkinson’s patients has found differences in the retina’s inner nuclear layer (INL). Previous studies have shown eye-scan data can reveal signs of other deterioration of neurological conditions like Alzheimer’s, multiple sclerosis and schizophrenia. The studies are part of an emerging field of research called “oculomics”. Eye scan data has also been shown to reveal people’s propensity to high blood pressure, heart disease, stroke and diabetes. Doctors have historically conducted physical eye tests, believing the organ can act as a “window” to the rest of the body, and provide direct insight into many aspects of human health. With high-resolution images of the retina now a routine part of eye care, scientists said the data from these scans can be put to better analysis to gain better insights on patient health. In particular, a type of 3D scan known as optical coherence tomography (OCT) is widely used in eye clinics and by high-street opticians. These scans can produce a cross-section of the retina – the screen of nerves at the back of the eye – in incredible detail down to a thousandth of a millimetre. Images of the retina can be extremely useful for monitoring eye health. But researchers said their value can become much more as a retinal scan is the only non-intrusive way to view layers of cells below the skin’s surface. They found in the new study that a reduced thickness of these cell layers was associated with an increased risk of developing Parkinson’s disease. Scientists have also started using powerful computers and AI technology to accurately analyse large numbers of OCTs and other eye images, in a fraction of the time it would take a human. “While we are not yet ready to predict whether an individual will develop Parkinson’s, we hope that this method could soon become a pre-screening tool for people at risk of disease,” study co-author Siegfried Wagner from the University College London said. “Finding signs of a number of diseases before symptoms emerge means that, in the future, people could have the time to make lifestyle changes to prevent some conditions arising, and clinicians could delay the onset and impact of life-changing neurodegenerative disorders,” Dr Wagner said. Researchers said the OCT method used in the study is also non-invasive of lower cost, more scalable and quicker than brain scans for this purpose. Read More Study could lead to injections that replicate brain benefits of exercise Dementia breakthrough as drug treatment comes one step closer Parkinson’s therapy could be used to tackle alcohol abuse Justin Trudeau slams Facebook for blocking news stories about wildfires Microsoft makes big changes to takeover of Activision Blizzard Meta could finally launch Threads feature everyone is waiting for
2023-08-23 16:16

Snap Appoints India Head, Announces Revamp in Growth Push
Snap Inc. is appointing a former Google executive to lead its India operations as it strives to become
2023-08-23 15:28

Tineco Presents the PURE ONE STATION at the IFA 2023 - Invitation to the Launch Event on September 1st, 2023
BERLIN--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 23, 2023--
2023-08-23 15:26

Yamaha’s CS-500 Now Certified for Microsoft Teams, Adding to Yamaha’s Portfolio of Certified Video Sound Collaboration Systems
HAMAMATSU, Japan--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 23, 2023--
2023-08-23 15:25

Tineco Unveils the Innovative Pure One Station at IFA 2023: Redefining Cleaning Excellence
PARIS--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 23, 2023--
2023-08-23 14:48
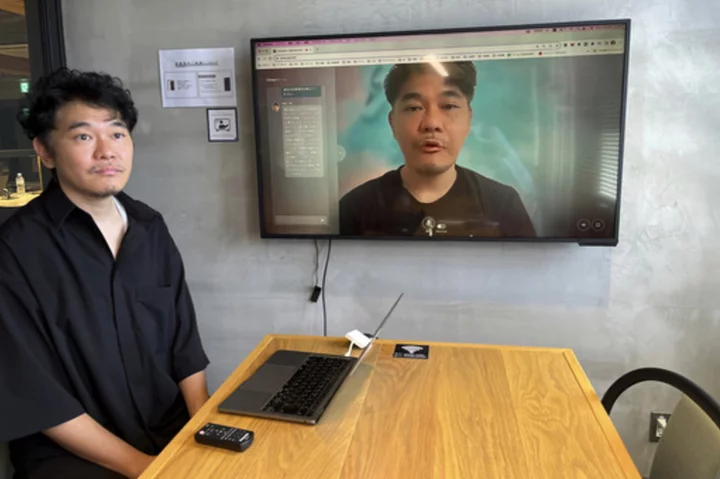
Digital clones and Vocaloids may be popular in Japan. Elsewhere, they could get lost in translation
Kazutaka Yonekura dreams of a world where everyone will have their very own digital “clone,” an online avatar that's updated in real time with information about a person's tastes and habits
2023-08-23 09:19
You Might Like...

Luminar and Plus Partner for LiDAR and AI-Based Assisted Driving Software for Trucking

Options Earns Distinction as Microsoft Solutions Partner for Data & AI Innovation

'There is no Coco Chanel': Lawsuit accuses Shein of copyright infringement

EU targets Apple, Amazon, Alphabet, ByteDance, Meta, Microsoft in next phase of digital crackdown

DNP Increases Number of Wide Range Coating Devices for High Function Optical Film at Mihara plant

Sierra Space’s Dream Chaser® Spaceplane Comes to Life

In EV battle, Toyota bets on new technology and old-school thinking
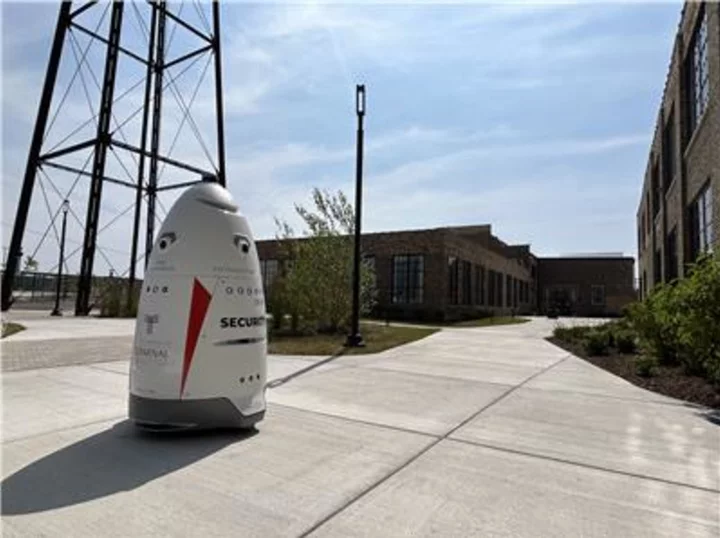

Knightscope K5 Now Patrolling in Windy City Urban Development
