
Inside China's underground market for high-end Nvidia AI chips
By Josh Ye, David Kirton and Chen Lin HONG KONG/SHENZHEN, China Psst! Where can a Chinese buyer purchase
2023-06-20 18:24

Huawei Kicks Off 2023 Tech Arena Competitions in Europe
PARIS--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 20, 2023--
2023-06-20 18:20

StrikeReady Named 2023 Startup of the Year at Globee Awards for American Business
PALO ALTO, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 20, 2023--
2023-06-20 18:19

Russia fines Telegram and Viber over war-related content
The companies behind the Telegram and Viber messaging apps were fined by a Moscow court on Tuesday for
2023-06-20 18:18
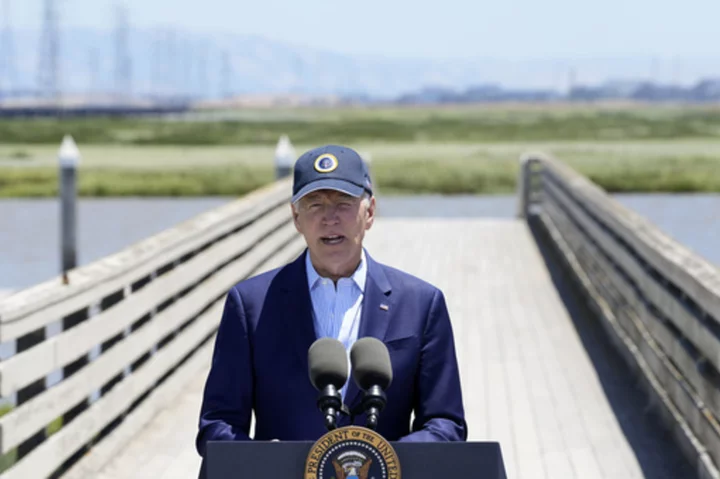

Biden will host a forum about artificial intelligence with technology leaders in San Francisco
President Joe Biden will convene a group of technology leaders in San Francisco to debate artificial intelligence
2023-06-20 17:25

iHeartMedia and Paris Hilton’s 11:11 Media Announce “The History of the World’s Greatest Nightclubs” Hosted by Ultra Naté
NEW YORK--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 20, 2023--
2023-06-20 17:22
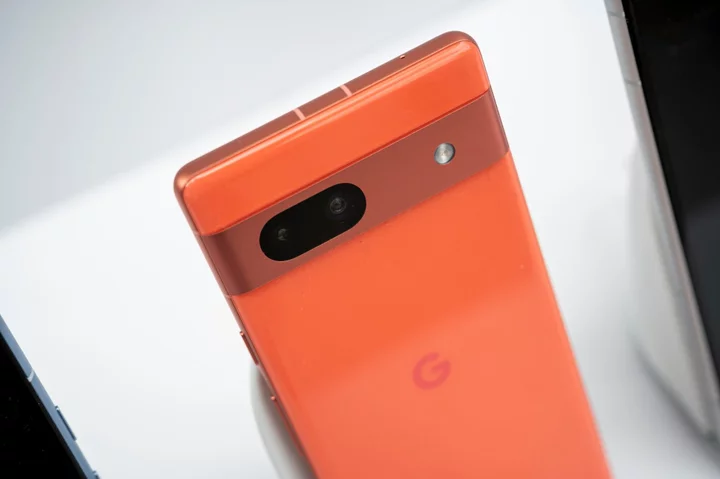

Google Seeks Suppliers to Move Some Pixel Production to India
Alphabet Inc.’s Google is scouting for suppliers in India to assemble its Pixel smartphones as it borrows from
2023-06-20 16:21

Scientists found the oldest water on the planet and drank it
If you found water that was more than two billion years old, would your first instinct be to drink it? One scientist did exactly that after finding the oldest water ever discovered on the planet. A team from the University of Toronto, led by Professor Barbara Sherwood Lollar, came across an incredible find while studying a Canadian mine in 2016. Tests showed that the water source they unearthed was between 1.5 billion and 2.64 billion years old. Given that it was completely isolated, it marked the oldest ever found on Earth. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Remarkably, the tests also uncovered that there was once life present in the water. Speaking to BBC News, professor Sherwood Lollar said: “When people think about this water they assume it must be some tiny amount of water trapped within the rock. “But in fact it’s very much bubbling right up out at you. These things are flowing at rates of litres per minute – the volume of the water is much larger than anyone anticipated.” Discussing the presence of life in the water, Sherwood Lollar added: “By looking at the sulphate in the water, we were able to see a fingerprint that’s indicative of the presence of life. And we were able to indicate that the signal we are seeing in the fluids has to have been produced by microbiology - and most importantly has to have been produced over a very long time scale. “The microbes that produced this signature couldn’t have done it overnight. This has to be an indication that organisms have been present in these fluids on a geological timescale.” The professor also revealed that she tried the water for herself – but how did it taste? “If you’re a geologist who works with rocks, you’ve probably licked a lot of rocks,” Sherwood Lollar told CNN. She revealed that the water was "very salty and bitter" and "much saltier than seawater." Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-06-20 14:58

Cambridge Broadband Networks Ltd. Africa and Tarana Announce Partnership to Equip Sub-Saharan Operators with Breakthrough Next-Gen Fixed Wireless
LAGOS, Nigeria & MILPITAS, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 20, 2023--
2023-06-20 14:24
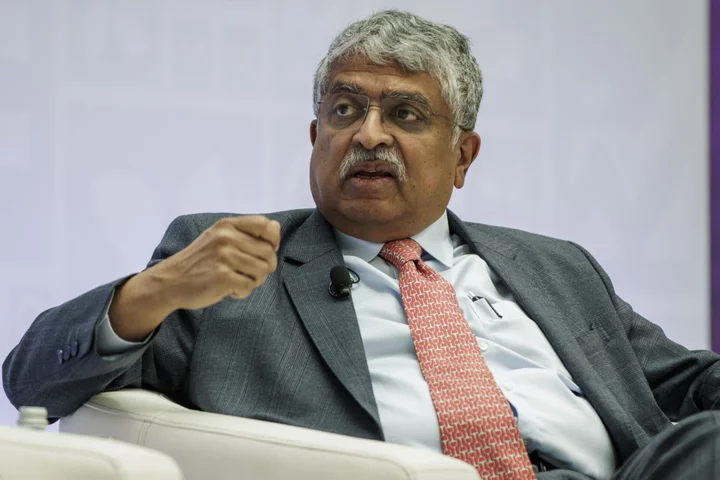

Billionaire Infosys Chair Gives Alma Mater $38.5 Million for AI
Billionaire Infosys Ltd. co-founder Nandan Nilekani will donate $38.5 million to his alma mater Indian Institute of Technology
2023-06-20 14:16

Scientists warn of threat to internet from AI-trained AIs
Future generations of artificial intelligence chatbots trained using data from other AIs could lead to a downward spiral of gibberish on the internet, a new study has found. Large language models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT have taken off on the internet, with many users adopting the technology to produce a whole new ecosystem of AI-generated texts and images. But using the output data from such AI systems to further train subsequent generations of AI models could result in “irreversible defects” and junk content, according to a new, yet-to-be peer-reviewed study. AI models like ChatGPT are trained using vast amounts of data pulled across internet platforms that have mostly remained human generated until now. But AI-generated data using such models have a growing presence on the internet. Researchers, including those from the University of Oxford in the UK, attempted to understand what happened when several subsequent generations of AIs are trained off each other. They found the widespread use of LLMs to publish content on the internet on a large scale “will pollute the collection of data to train them” and lead to “model collapse”. “We discover that learning from data produced by other models causes model collapse – a degenerative process whereby, over time, models forget the true underlying data distribution,” scientists wrote in the study, posted as a preprint in arXiv. The new findings suggested there to be a “first mover advantage” when it comes to training LLMs. Scientists liken this change to what happens when AI models are trained on music created by human composers and played by human musicians. The subsequent AI output then trains other models, leading to a diminishing quality of music. With subsequent generations of AI models likely to encounter poorer quality data at their source, they may start misinterpreting information by inserting false information in a process scientists call “data poisoning”. They warned that the scale at which data poisoning can happen drastically changes after the advent of LLMs. Just a few iterations of data can lead to major degradation, even when the original data is preserved, scientists said. And over time, this could lead to mistakes compounding and forcing models that learn from generated data to misunderstand reality. “This in turn causes the model to misperceive the underlying learning task,” researchers said. Scientists cautioned that steps must be taken to label AI-generated content from human-generated ones, along with efforts to preserve original human-made data for future AI training. “To make sure that learning is sustained over a long time period, one needs to make sure that access to the original data source is preserved and that additional data not generated by LLMs remain available over time,” they wrote in the study. “Otherwise, it may become increasingly difficult to train newer versions of LLMs without access to data that was crawled from the Internet prior to the mass adoption of the technology, or direct access to data generated by humans at scale.” Read More ChatGPT ‘grandma exploit’ gives users free keys for Windows 11 Protect personal data when introducing AI, privacy watchdog warns businesses How Europe is leading the world in the push to regulate AI ‘Miracle material’ solar panels to finally enter production Meta reveals new AI that is too powerful to release Reddit user’s protests against the site’s rules have taken an even more bizarre turn
2023-06-20 13:57

Alibaba appoints Joseph Tsai, Eddie Wu to succeed Daniel Zhang as chairman and CEO
Joseph Tsai, executive vice chairman and cofounder of Alibaba Group, will succeed Daniel Zhang as chairman, according to an announcement by the Chinese internet giant on Tuesday.
2023-06-20 13:16
You Might Like...

BII, ILX to Co-Fund $500 Million of Sustainable Development

HyperX Announces Exclusive Collaboration with Team Liquid for Custom “Blue” Mascot Keycap

Earthbound solar storm could cause 'internet apocalypse'

Japan to open up Apple- and Google-dominated phone apps to competition

Netflix ad tier now has nearly 5 million monthly active users
Fourth’s HotSchedules Named Leading Employee Scheduling and Workforce Management Solution

Silver Hill Hospital Names Dr. Mark J. Russ as Chief Medical Officer

Thousands of Reddit communities go dark to boycott third-party app charges
