
Sony Unveils Slimmer New PlayStation 5 With Detachable Disc Drive
Sony Group Corp. has unveiled a slimmer, lighter PlayStation 5 with detachable disc drive, in a bid to
2023-10-12 11:51

The world will pay a high price if China cuts off supplies of chipmaking materials
Just one month after China announced it would curb exports of germanium and gallium, both essential for making semiconductors, its overseas shipments of the materials fell to zero.
2023-10-12 08:20

Microsoft to appeal IRS request for nearly $29 billion in back taxes
Microsoft plans to contest a US Internal Revenue Service request for an additional $28.9 billion in back taxes for the years 2004 to 2013, the company said in a securities filing Wednesday.
2023-10-12 05:29

Parents urged to delete their kids social media accounts ahead of possible Israeli hostage videos
Schools in Israel, the UK and the US are advising parents to delete their children's social media apps over concerns that Hamas militants will broadcast or disseminate disturbing videos of hostages who have been seized in recent days.
2023-10-12 05:24

NY officials announce legislation aimed at protecting kids on social media
Two new bills meant to protect children's mental health online by changing the way they are served content on social media and by limiting companies' use of their data will be introduced in the New York state legislature, state and city leaders said Wednesday.
2023-10-12 03:57
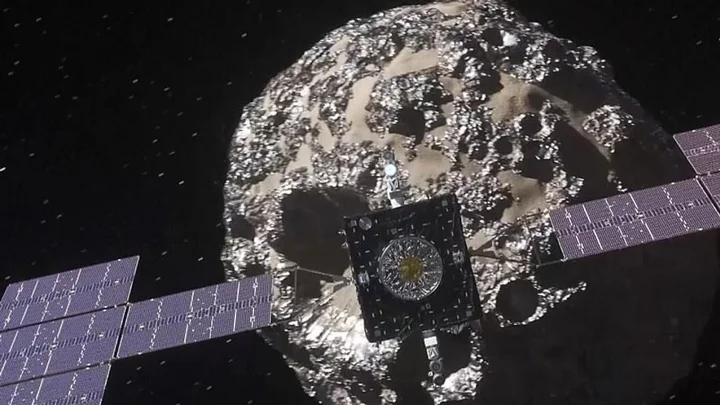

NASA releases first photos and findings from Bennu asteroid sample
NASA has lifted the lid on its first findings about the Bennu sample, one of the "most hazardous known asteroids". The highly-anticipated sample from the OSIRIS-REx’s mission took seven years to complete and finally made a safe landing on Sunday 24 September. Scientists audibly gasped upon opening the capsule. They kept details to a minimum and maintained a slow pace in progress for "good reason," as they received more material than expected. "The abundance of material found when the science canister lid was removed earlier this week has meant that the process of disassembling the TAGSAM (Touch-and-Go Sample Acquisition Mechanism) head – which holds the bulk of material from the asteroid – is off to a methodical start," they said a the time. That was until now... On Wednesday 11 October, the space agency shared details for the first time from NASA experts and the University of Arizona. NASA said there were signs of water and carbon on the sample through hydrated clay minerals that contain carbon. "At nearly 5% carbon by weight, carbon being the central element of life, far exceeding our goal of 60g, this is the biggest carbon-rich asteroid sample ever returned to earth," Administrator Bill Nelson said, adding that it was "exactly the kind of material that we wanted to find." He went on to suggest that "they are going to help us determine the origin of elements that could have led to life" and provide a greater understanding of how to protect Earth from asteroids. Scientists also revealed that the sample contained space dust from asteroid Bennu. NASA showed the audience the sample on a video to protect the sample and to prevent contamination. Speaking about working through a glove box to analyse the sample, Francis McCubbin, astronomical curator at NASA's Johnson Space Centre said: "[It is] "hard, challenging work, and it does not go quickly, but we need to do this right". The samples will be preserved so that "scientists that aren't even born yet are going to have the opportunity to answer questions about our universe with these samples using technology that has not even been invented." Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-10-12 00:21
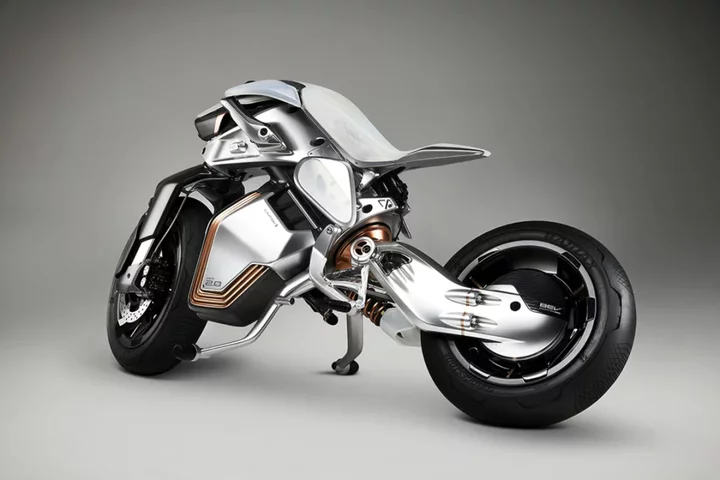

Yamaha unveils self-riding motorbike with no handlebars
Yamaha has unveiled a self-riding electric motorbike that features no handlebars or other standard controls. The Yamaha Motoroid 2 is the next generation of the firm’s Motoroid concept bike first revealed in 2017, but unlike its predecessor, Yamaha has built a working prototype of the latest vehicle. The self-balancing bike features gyroscopes and image recognition AI systems to stay upright and navigate roads, while also being capable of riding itself without anyone aboard. “Motoroid 2 is a vehicle for personal mobility that can recognise its owner, get up off its kickstand and move alongside its rider,” the company said. “[It] has a distinctly lifelike feel when somebody is riding on its back and has a presence more like a lifetime companion.” Yamaha plans to show off the prototype of the Motoroid 2 at the Events Japan Mobility Show 2023 in Tokyo next month. It is not clear whether Yamaha plans to release a production model of the bike, however its continued development suggests that the automotive giant is working to integrate at least some of its features into future motorcycles. Self-driving technology is increasingly common in production vehicles, though it is currently limited to four-wheeled cars and trucks. Some have even considered eschewing steering wheels, with Tesla chief executive Elon Musk originally planning to build a fleet of self-driving electric taxis that have no visible user controls. The plan was reportedly sidelined after company executives noted that regulators in most major markets require steering wheels and pedals on vehicles. Several motorcycle manufacturers have unveiled concept bikes that require no rider to operate. BMW’s ConnectedRide retrofits the company’s R 1200 GS Adventure with autonomous technology to serve as a “testbed for advanced motorcycle safety” equipment that it hopes to introduce to its production models. “In a future world of autonomously driving cars, being connected will be an urgent requirement for all motorcycle segments,” BMW’s Markus Schramm said in 2020. “This will enhance safety and ensure that motorcycling remains future-proof.” Read More Reinventing the seatbelt for the self-driving era
2023-10-11 23:49

Mystery signals coming from space might finally have been explained by ‘starquakes’
Mysterious blasts coming from deep in space could be the result of “starquakes”, according to a new study. For years, scientists have been observing fast radio bursts, or FRBs, coming from distant parts of space. They are very intense, very short blasts of energy – and despite finding many of them, researchers still do not know where they are coming from or how they might be formed. Now, scientists have spotted that there is appears to be similarities between those FRBs and earthquakes. Researchers behind the new study suggest that the blasts could be the result of similar behaviour on neutron stars, known as starquakes. It is just one possible explanation for the unusual bursts, which have led to suggestions they could be anything from neutron stars colliding with black holes to alien technology. Most have settled on the belief that at least some of those FRBs come from neutron stars, however, which are formed when supergiant stars collapse into an incredibly dense, small object. In the new study, researchers looked at data from nearly 7,000 bursts, taken from three different sources that are sending out repeated FRBs, examining the time and energy that they emerged in. They then also looked at earthquake information taken from Japan, and data on solar flares, and looked to compare the three. There was little connection between FRBs and solar flares, the researchers found. But there was a striking similarity between the blasts and earthquakes. “The results show notable similarities between FRBs and earthquakes in the following ways: First, the probability of an aftershock occurring for a single event is 10-50%; second, the aftershock occurrence rate decreases with time, as a power of time; third, the aftershock rate is always constant even if the FRB-earthquake activity (mean rate) changes significantly; and fourth, there is no correlation between the energies of the main shock and its aftershock,” said Tomonori Totani from the University of Tokyo, one of the leaders of the study. The findings have led scientists to speculate that there is a solid crust on the outer surface of neutron stars. That crust then experiences starquakes in the same way the Earth’s surface does – and those quakes then let out powerful blasts of energy that make their way to us as FRBs. But researchers say they will need to further examine those FRBs to better understand the connection between the two – as well as to help give us information about quakes and other physical phenomena that are closer to home. “By studying starquakes on distant ultradense stars, which are completely different environments from Earth, we may gain new insights into earthquakes,” said Professor Totani. “The interior of a neutron star is the densest place in the universe, comparable to that of the interior of an atomic nucleus. “Starquakes in neutron stars have opened up the possibility of gaining new insights into very high-density matter and the fundamental laws of nuclear physics.” The research is described in a new paper, ‘Fast radio bursts trigger aftershocks resembling earthquakes, but not solar flares’, published in the journal Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
2023-10-11 23:26

Scientist publishes 'evidence' that we really could all be living in the Matrix
“The Matrix is everywhere. It is all around us. Even now in this very room." So says Laurence Fishburne’s Morpheus in sci-fi classic ‘The Matrix’ as he offers Keanu Reeves’s Neo the choice to find out just how “deep the rabbit hole goes”. Now, just as Neo discovered that the "life" he'd been living was little more than an algorithmic construct, scientists and philosophers are arguing that we could be stuck inside a simulation ourselves. In a paper published earlier this month, physicist Melvin Vopson, of the University of Portsmouth, offered scientific evidence for a philosophical theory known as the simulation hypothesis. This, in a nutshell, posits that the entire universe and our objective reality are just super-advanced virtual reality illusions. Elon Musk is among the well-known fans of the theory, which – as Dr Vopson notes in his paper – has been “gaining traction in scientific circles as well as in the entertainment industry”. The university lecturer also pointed out that recent developments in a branch of science known as information physics “appear to support this possibility”. Information physics suggests that physical reality is fundamentally made up of bits of information. However, Dr Vopson has gone further and is working to prove that information has a physical mass and is a fundamental building block of the universe. He even claims that information could be the mysterious dark matter that makes up almost a third of the universe. In previous research, the physicist proposed that all elementary particles (the smallest known building blocks in the universe), store information about themselves, much like DNA in humans. Then, in 2022, he discovered a new law of physics, christened the second law of infodynamics, which states that entropy – the degree of randomness or disorder – within an isolated information system either remains constant or decreases over time. In other words, the system becomes less and less chaotic, implying that there is some kind of mechanism governing it rather than random chance. “I knew then that this revelation had far-reaching implications across various scientific disciplines,” Dr Vopson said in a statement released by the University of Portsmouth. “What I wanted to do next is put the law to the test and see if it could further support the simulation hypothesis by moving it on from the philosophical realm to mainstream science.” Is the Universe a Simulation? | Melvin Vopson www.youtube.com Dr Vopson employed the law in a range of different fields, including genetics, cosmology and even symmetry. Here, he found that the abundance of symmetry in the Universe (think snowflakes and facial structures) could be explained by the second law of infodynamics. "Symmetry principles play an important role with respect to the laws of nature, but until now there has been little explanation as to why that could be,” he said. “My findings demonstrate that high symmetry corresponds to the lowest information entropy state, potentially explaining nature's inclination towards it." Again, put simply, nature prefers things to be as well-ordered as possible. He continued: “This approach, where excess information is removed, resembles the process of a computer deleting or compressing waste code to save storage space and optimise power consumption.” As a result, this “supports the idea that we’re living in a simulation.” Dr Vopson is serious about this idea and, last year, even launched a crowdfunding campaign to test it. At the time, he announced that he had designed an experiment to determine whether we are all just characters in an advanced virtual world. “There is a growing community out there looking seriously at the possibility that information is more fundamental to everything than we think,” he said in a statement released back in December. “If information is a key component of everything in the universe, it would make sense that a vast computer somewhere is in control. “Assuming the universe is indeed a simulation, then it must contain a lot of information bits hidden everywhere around us. I’ve devised an experiment that proposes a way of extracting this information to prove it’s there.” His proposed experiment is based on his conclusion that information is physical and that elementary particles have a DNA of information about themselves. He posited that the information in an elementary particle could be detected and measured by using particle-antiparticle collision. “We can measure the information content of a particle by erasing it. If we delete the information from the particles, we can then look at what’s left,” he said in the December statement. “This experiment is highly achievable with our existing tools, and I’m hoping the crowdfunding site will help us achieve it.” And whilst the crowdfunder closed well before reaching its proposed £185,000 target, Dr Vopson still hopes to carry out the ambitious test. Following his most recent paper, he suggested the experiment had the power to confirm the “fifth state of matter in the universe” and “change physics as we know it.” Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-10-11 23:00
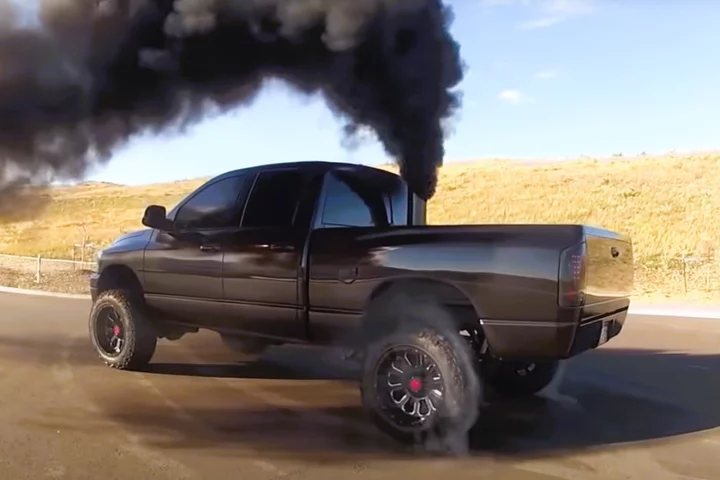

Ebay faces $2 billion fine for ‘rolling coal’ sales
Ebay is facing a fine of nearly $2 billion for allegedly enabling the sale of ‘rolling coal’ devices and other deliberately polluting equipment that violates environmental laws. The US Department of Justice alleges that the online retailer sold more than 343,000 so-called defeat devices in violation of the Clean Air Act, with each sale the subject of a $5,580 fine. Rolling coal has become a form of anti-environmentalism protest in the United States, involving the modification of a diesel engine in order to emit black clouds of sooty exhaust fumes. Online video compilations show drivers of pickup trucks deliberately rolling coal as they pass cyclists and electric vehicles. Until recently, the devices required to perform it were relatively easy to find through online retailers, costing between $200-500. The Justice Department wrote in its complaint, which was filed on behalf of the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in a federal court in New York, that the rolling coal devices “defeat motor vehicle emission controls” set out in the Clean Air Act. “Aftermarket defeat devices significantly increase pollution emissions – including carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, particulate matter and nonmethane hydrocarbons – that harm public health,” the complaint stated. The EPA criminalised the practice, which appears to be mainly confined to the US, in 2014, with some states warning of fines of up to $5,000 for anyone caught doing it. Several companies who sell coal rolling equipment have already been forced to pay fines of up to $1 million for breaking the law. “Our nation’s environmental laws protect public health and the environment by prohibiting the unlawful sales of defeat devices; unregistered, misbranded and restricted use pesticides; and unsafe products containing toxic chemicals,” David Uhlmann from the EPA’s Office of Enforcement and Compliance Assurance said following the Justice Department’s latest action against eBay. “The complaint filed demonstrates that EPA will hold online retailers responsible for the unlawful sale of products on their websites that can harm consumers and the environment.” Ebay described the lawsuit as “entirely unprecedented”, claiming that sales of such devices were banned and that it was actively policing its site against their sale. “Maintaining a safe and trusted marketplace for our global community of sellers and buyers is a fundamental principle of our business,” the company said. “Indeed, eBay is blocking and removing more than 99.9 per cent of the listings for the products cited by the DOJ, including millions of listings each year.” Read More World’s first solar powered hybrid truck tested on public roads Why is Elon Musk obsessed with the letter X? How Elon Musk’s Twitter became a haven for fake news and misinformation Viral WhatsApp warning of cyberattack targeting Jewish people is fake
2023-10-11 21:20

Google is about to ditch passwords forever
Google has announced that its apps and services will now be “passwordless by default” in an effort to make all users switch to passkeys. The move is part of a broader consensus among the tech industry to ditch passwords, which have been around since the 1960s, and switch to a safer and more efficient format to verify a person’s identity. Passkeys combine a code with biometric information like a fingerprint or facial recognition, making them easier to remember and harder to be stolen. Google apps like YouTube, Search and Maps all support the new format after it was first introduced earlier this year, though take up has been slower than expected. The tech giant said the push to get users to adopt passkeys coincided with Cybersecurity Awareness Month, claiming that the new technology is faster and more secure. “They are 40 per cent faster than passwords – and rely on a type of cryptography that makes them more secure,” Google product managers Sriram Karra and Christiaan Brand wrote in a blog post explaining the move. “We’ll continue encouraging the industry to make the pivot to passkeys – making passwords a rarity, and eventually obsolete.” Google users who do not already use passkeys will receive a prompt to set one up the next time they sign into their account. Passkeys have already been enabled by other online platforms, including eBay and Uber, as the tech industry looks to completely transition away from traditional passwords. “We’ve seen great results from launching passkeys across our apps and encourage all users to adopt passkeys,” said Ramsin Betyyousef, a senior director of engineering at Uber. “Ultimately this is a win-win for Uber and Uber’s customers.” Google, which counts billions of users across all of its platforms, acknowledged that “new technologies take time to catch on”, and have therefore given people the option to temporarily opt out of passkeys and use passwords wherever possible. The company did not set a date for when passwords will be phased out entirely, but some security experts contend that their death is inevitable while hackers continue to exploit their vulnerability. Helping implement the transition is the FIDO (Fast Identity Online) Alliance, which has been working with Apple, Google, Microsoft and hundreds of tech companies to develop the new login standard. “The complete shift to a passwordless world will begin with consumers making it a natural part of their lives,” said Alex Simons, who heads Microsof’s Identity Program Management team. “By working together as a community across platforms, we can at last achieve this vision and make significant progress toward eliminating passwords.” Read More Pixel 8: Google unveils ‘AI-centred’ iPhone rival Google to trial AI in UK traffic light systems to reduce stop-and-go emissions Pixel 8: Google unveils DeepMind-powered iPhone rival China’s discovery of never-before-seen ore could propel battery technology
2023-10-11 18:21
China’s discovery of never-before-seen ore could propel battery technology
A never-before-seen ore containing vast quantities of an element widely used in semiconductors has been found in China in a discovery that could propel new advances in battery technology. Geologists found rare earth metal niobium inside the new ore named niobobaotite from north China’s Inner Mongolia. The rare earth metal is widely used in alloys for jet engines and rockets and has also been shown to have exceptional current conducting properties in low temperatures. Some researchers have said batteries made from niobium have several advantages over traditional lithium-ion batteries. The main source of niobium until now has been from the ore mineral columbite that is extracted widely in Canada, Brazil, Australia and Nigeria, with China obtaining nearly 95 per cent of the element for its steel industry via imports. If geologists can prove that sufficient volume and quality of niobium can be extracted from niobobaotite, experts said it could help make China “self-sufficient”, reported the South China Morning Post newspaper. The niobobaotite ore has received official approval from the International Mineralogical Association’s classification committee, according to the China National Nuclear Corporation, a state-run enterprise responsible for overseeing China’s civilian and military nuclear programmes. The Brazilian Metallurgy and Mining Company (CBMM) has been working on new projects towards the use of niobium to make advanced lithium-ion batteries. China’s state news agency Xinhua reported earlier this year that CBMM is partnering with universities, research centres and battery makers to improve the use of the rare earth element in lithium batteries. Niobium batteries are expected to bring several advantages over traditional lithium-ion batteries that tend to pose challenges like safety risks, short life cycles and long charging times, Antonio Castro Neto, director of the National University of Singapore’s Centre for Advanced 2D Materials, said earlier this year. “We have made significant progress in our development of niobium-graphene batteries which are proving to be a game changer in safety, efficiency, and sustainability,” Dr Neto said. Researchers said the performance duration of niobium-graphene batteries can be 10 times longer than traditional lithium-ion batteries, thus making them last for an estimated 30 years and make them more durable and reliable as well. These batteries, currently in development, can also be fully charged in less than 10 minutes, they said. “As they have a longer lifespan, the new graphene-niobium batteries significantly reduce total cost of ownership compared to existing lithium-ion batteries and have ultrafast charging capabilities. In addition, they offer higher safety as they do not risk explosion even in high temperatures,” Rogerio Ribas, CBMM’s global head of batteries, said in a statement. Read More China’s ‘government-approved’ AI chatbot says Taiwan invasion is likely Australian-Chinese journalist detained for 3 years in China returns to Australia Driver killed after crashing into Chinese consulate in San Francisco had knives and crossbow EU asks Elon Musk to ‘walk the talk’ on X/Twitter disinformation over Hamas attack Earth hit by a huge solar storm that would devastate civilisation, trees show Viral WhatsApp warning of cyberattack targeting Jewish people is fake
2023-10-11 15:51
You Might Like...

Exclusive-AI chip startup d-Matrix raises $110 million with backing from Microsoft

PlayStation Project Q: New console will let people stream PS5 games on the move, Sony says

NeoCurrency Taps Gift Card Agency Vet Eric Thiegs to Accelerate Growth and Innovation
Paige Applies the Power of AI to Improve Breast Cancer Diagnoses with the Launch of its Expanded Breast Suite

Intel to invest $25 billion in Israel factory in record deal, Netanyahu says

Villanova University Names Raymond D. Duffy Vice President for Human Resources

Meta Fined Record €1.2 Billion in EU Over US Data Transfers
‘Miracle material’ solar panels to finally enter production in China
