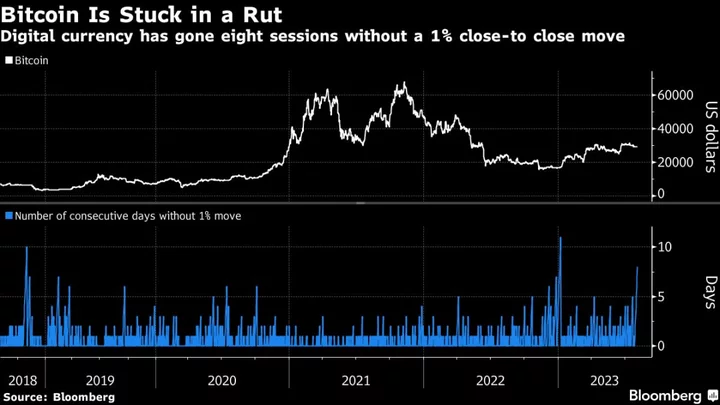
Bitcoin Loses Mojo After First-Half Rally Fails to Reignite Enthusiasm
Chalk it up to the heat, to late-summer doldrums, or to the phases of the moon, but the
2023-08-05 02:19

Apex Legends Season 18 Dive Trails Rewards Replaced
What will Respawn Entertainment replace Dive Trails with?
2023-08-05 01:51

Don’t Let Peach Season Pass Without Making This Rustic Cobbler
August is peach season, and this cobbler is one of the simplest desserts to make with the stone fruit.
2023-08-05 01:45
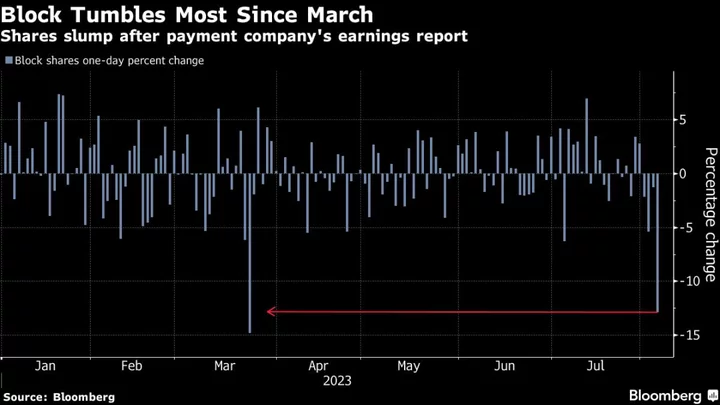
Block Shares Drop Most Since March After Earnings Disappointment
Block Inc., Jack Dorsey’s payments company, tumbled as much as 14% after reporting results that fell short of
2023-08-05 01:15
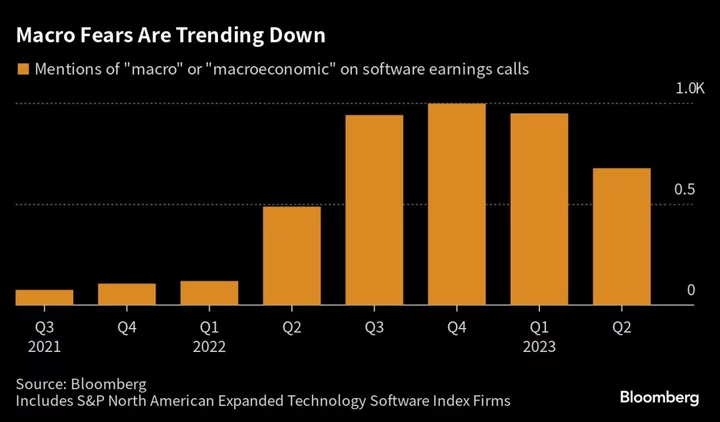
Cloud Services Industry Shows Early Signs of a Comeback
Cloud services companies are rallying as earnings reports suggest the wave of spending cuts that had hammered the
2023-08-05 00:55

A crispy roast potatoes recipe could be the key to life on Earth
A chemical reaction that gives food flavour could have helped evolution, one study suggests. According to New Scientist, the Maillard reaction is when the temperature between sugars and amino acids rises above approximately 140°C. It often occurs in food such as toasted bread, meats and roasted vegetables. Caroline Peacock at the University of Leeds wanted to explore whether it could happen at lower temperatures. To do this, scientists added iron or manganese minerals to a solution made up of sugar glucose and the amino acid glycine. When the substance was incubated at 10°C, the process was sped up by around 100 times. The temperature is said to be similar to the seabed at the edges of continents. Peacock and the team discovered that the Maillard reaction also occurs on the ocean floor, where iron and manganese minerals are often found. If this is the case, it could cause the carbon in sugars and amino acids to be stored in "large, complex polymers that microbes find harder to ingest," Peacock said, as per the publication. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter "If you can get your carbon through the 1-metre danger zone [at the top of the sea floor], where carbon generally is attacked and degraded and turned back into carbon dioxide by microbes, that will lock it away from the atmosphere," she explained. The team estimated that the minerals could lock away roughly 4 million tonnes of carbon every year. If this process didn't exist, the atmosphere could have warmed by a further 5°C over the past 400 million years, the study suggested. "This process has such a profound impact on atmospheric oxygen," she says. "Because complex life forms require higher levels of oxygen, as they’re more energetically demanding, we think it’s reasonable to surmise this process had a hand in creating conditions required for complex life." Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-05 00:28

Say Your Goodbyes: Microsoft Begins the Cortana for Windows Shutdown
So long, Cortana. Microsoft is retiring the voice assistant’s Windows app this month. The company
2023-08-04 23:49
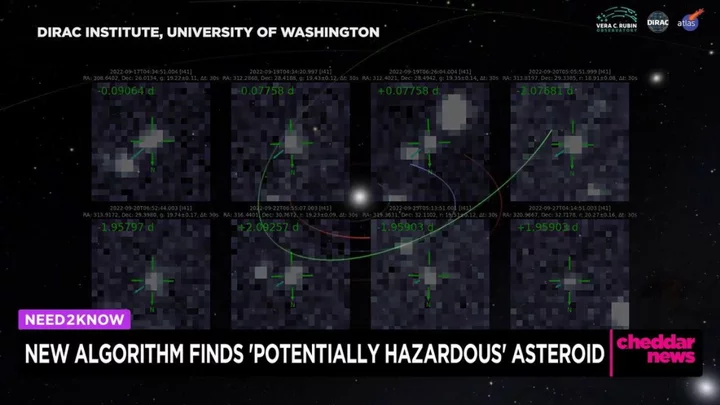
AI spots dangerous asteroid heading towards Earth that scientists missed
So far this year, we’ve mostly been seeing artificial intelligence pop up on our timelines as a tool for creating trivial things like odd news songs from classic bands or bizarrely sexualised images of classic artworks However, it looks like AI had a vital practical implementation recently after spotting a dangerous asteroid heading close to Earth that was originally missed by scientists. A 600-foot asteroid named 2022 GN1 was found thanks to a new algorithm, and it was revealed that our planet had a close shave with the object last year. As it’s now been revealed, 2022 GN1 flew a relatively close 4.5 million miles from Earth in September 2022. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter It sounds like a huge distance, but it falls within the definition of a potentially hazardous asteroid (PHA). At the time, it was completely missed due to it being obscured by starlight from objects in the Milky Way. The algorithm, named HelioLinc3D, spotted the object after observing data from the Zwicky Transient Facility (ZTF) telescope. The team leader behind the algorithm, Mario Jurić, released a statement saying: “This is just a small taste of what to expect with the Rubin Observatory in less than two years, when [the algorithm] HelioLinc3D will be discovering an object like this every night. “But more broadly, it’s a preview of the coming era of data-intensive astronomy. From HelioLinc3D to AI-assisted codes, the next decade of discovery will be a story of advancement in algorithms as much as in new, large, telescopes.” Meanwhile, scientists think they have come up with a new approach to mitigating global warming: put up a giant “umbrella” in space to protect the Earth from excess sunlight. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-04 23:22

Google update makes it easier for US users to remove some unwanted search results
Google unveiled new privacy updates this week that lets US users have a wee bit more control over the search results that pop up about themselves online.
2023-08-04 23:22

Summer Heat Waves Are Far From Over in the Mediterranean Sea
Add unprecedented sea temperatures in the Mediterranean to the grim list of heat-related records being smashed this summer.
2023-08-04 22:57

Morgan Stanley Reaches 70% of $1 Trillion ESG Funding Goal
Morgan Stanley said it’s more than two thirds of the way towards achieving its target to finance $1
2023-08-04 22:17
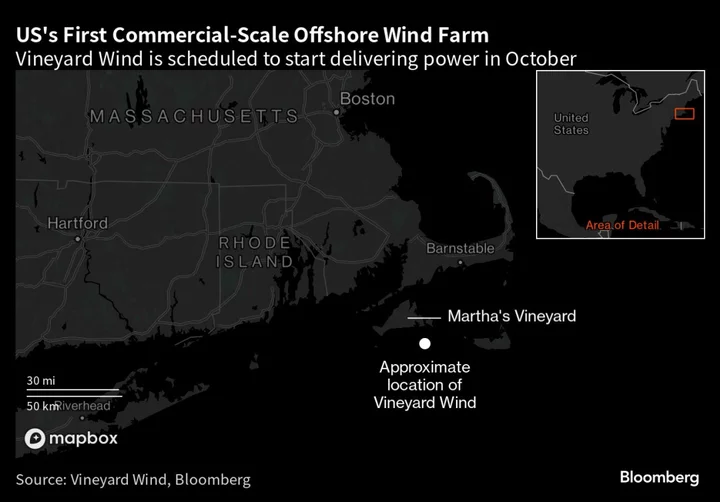
World’s Biggest Offshore Wind Turbine to Rise Next Week in US
About 15 miles south of Martha’s Vineyard, Massachusetts, a massive structure emerges from the Atlantic Ocean. Nearby it
2023-08-04 21:26
